May 18, 2021 | Nora Samaranayake
Innate Immunity Created by Live Attenuated Vaccines Like Measles and Polio May Provide Some Protection Against Future Pandemics – Idea Needs To Be Tested, Scientists Say
Institute of Human Virology at the University of Maryland School of Maryland scientists, who are also members of the Global Virus Network (GVN), a coalition comprised of human and animal virologists from 63 Centers of Excellence and 11 Affiliates in 35 countries, and colleagues today published a perspective proposing that live attenuated vaccines (LAVs), such as those for tuberculosis, measles, and polio, may induce protective innate immunity that mitigate other infectious diseases, triggering the human body’s natural emergency response to infections including COVID-19 as well as future pandemic threats.
The scientists suggest that LAVs prospectively might offer a vital tool to bend the pandemic curve, averting the exhaustion of public health resources and preventing needless deaths, and merit being studied. The perspective was published in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America (PNAS).
“A review of epidemiological, clinical and biological evidence suggests that induction of innate immunity by existing LAVs, that is, the broadly effective vaccines, can protect against unrelated infections such as coronavirus, and could be used to control epidemics caused by emerging pathogens,” said Dr. Robert Gallo, The Homer & Martha Gudelsky Distinguished Professor in Medicine, Co-Founder & Director of the Institute of Human Virology at the University of Maryland School of Medicine, and Co-Founder & Chairman of the International Scientific Leadership Board of the Global Virus Network.
 Dr. Gallo said, “This approach is worthy of prompt further study due to the probability of future pandemics. This could be a stop-gap before specific vaccines are made. But even in the current pandemic they may be of use in non-affluent nations where the specific vaccines are not available.
Dr. Gallo said, “This approach is worthy of prompt further study due to the probability of future pandemics. This could be a stop-gap before specific vaccines are made. But even in the current pandemic they may be of use in non-affluent nations where the specific vaccines are not available.
“Our innate immune response is the first line of defense against invading, new pathogens. The outcome of any infection depends on the race between the pathogen and the host defense systems. The innate immunity and enhancing defense pathways provided by widely-used and well-recognized vaccines could substantially mitigate, or even prevent, infection from other pathogens such as SARS-CoV-2. This is especially valuable because LAVs can fill the gap until specific vaccines are available and in particular when they have not reached certain countries globally.”
“We very actively support the marvelous COVID-19-specific vaccines, and nothing in this publication conflicts with the development and use of these effective vaccines,” said Dr. Michael Avidan of the Department of Anesthesiology, Washington University, St Louis, MO. “We are suggesting that in the absence or availability of pathogen-specific vaccines, particularly in the beginning phase of a pandemic, that LAVs be rigorously tested to determine whether they can control infection and disease progression.”
“LAVs are safe, cheap and proven effective strategy to curtail the COVID-19 pandemic in two ways,” said Dr. Shyam Kottilil, Professor of Medicine and Director, Division of Clinical Care and Research, Institute of Human Virology at the University of Maryland School of Medicine, GVN Center of Excellence. “By offering immediate protection against infection with SARS CoV-2 mediated by enhanced innate immunity and boosting immune response to traditional vaccine against COVID19 working as an adjuvant.”
 “Even in the case of a microorganism such as SARS-CoV-2, for which we have been able to develop vaccines fairly quickly, it is still a minimum of one and a half to two years until a safe and effective vaccine can be produced, tested, distributed, and delivered globally,” said Dr. Dean Jamison, a leading global health economist of the Institute for Global Health Sciences, University of California, and the GVN. “In this period, countless lives have been lost and economic havoc has been unleashed in the world economy. This could be even more tragic in the case of a future pandemic for which the development of a vaccine is more challenging, transmission is more rapid, or herd immunity more difficult to achieve. LAVs that stimulate innate immunity could serve as a stop-gap until an effective vaccine is widely available.”
“Even in the case of a microorganism such as SARS-CoV-2, for which we have been able to develop vaccines fairly quickly, it is still a minimum of one and a half to two years until a safe and effective vaccine can be produced, tested, distributed, and delivered globally,” said Dr. Dean Jamison, a leading global health economist of the Institute for Global Health Sciences, University of California, and the GVN. “In this period, countless lives have been lost and economic havoc has been unleashed in the world economy. This could be even more tragic in the case of a future pandemic for which the development of a vaccine is more challenging, transmission is more rapid, or herd immunity more difficult to achieve. LAVs that stimulate innate immunity could serve as a stop-gap until an effective vaccine is widely available.”
“Besides protecting against infection, innate immunity stimulation also has the potential to be used therapeutically in the early stages of disease, as well as to boost the effectiveness of vaccines that promote a specific adaptive immune response. This potential, while theoretical, is also worthy of further study,” said Dr. Konstantin Chumakov, Associate Director for Research for the U.S. Food and Drug Administration’s (FDA) Office of Vaccines Research and Review, and a GVN Center Director. “As we wrote last year in a perspective published in Science, studies with the oral poliovirus vaccine (OPV) from the 1960s and 1970s demonstrated nonspecific immune protection and found that OPV reduced the incidence of seasonal influenza and acute respiratory disease.”
In 2014, a World Health Organization (WHO)-commissioned review at the recommendation of the Strategic Advisory Group of Experts on vaccines (SAGE) concluded that LAVs reduced child mortality by more than expected. The same patterns were observed in high-income settings, including in the U.S., as having a live vaccine as the most recent vaccine being associated with a halving of the risk of hospitalization for non-targeted infections. The WHO review advised more research regarding the beneficial heterologous effects of LAVs; to date, no such WHO studies have been conducted.
The authors said that because of the huge toll that the current pandemic has taken on a global basis, looking into all possible options is essential. Despite the unprecedented brief time that it took to develop, test and deliver the current vaccines, it still took a year and a half and if LAVs could help stimulate innate immunity, they could help delay the global impact of a new pandemic while a new vaccine is being developed.
“There is immense readiness and massive financial support to develop and deliver the novel specific vaccines, but very little to test LAVs for use during a pandemic, despite their potential to prevent needless suffering and help mitigate social and economic carnage in any future pandemic. There are even some advantages in that they work very promptly, are low cost and likely to be readily available. Furthermore, their safety profile is often well-established. But we must acknowledge there are likely limitations because they do not last very long, perhaps only a few months," said Dr. Gallo.
“My esteemed colleagues and I are urgently calling on governments, philanthropy and non-profit foundations to support testing of an LAV strategy to determine whether LAVs can protect high-risk populations such as healthcare workers and the elderly as well as low-income populations worldwide, thereby reducing social and economic inequities.”
In addition to Dr. Robert Gallo, Dr. Konstantin Chumakov, Dr. Michael Avidan, Dr. Shyam Kottilil, and Dr. Dean Jamison, the authors of the PNAS viewpoint include Dr. Christine Benn of the Department of Clinical Research, GVN Center of Excellence, University of Southern Denmark; Dr. Mihai Netea of the Department of Internal Medicine and Radboud Center for Infectious Diseases, Radboud University Medical Center, a GVN Center of Excellence; Dr. Annie Sparrow of the Department of Population Health Science and Policy, Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai; Dr. Stefano Bertozzi of the School of Public Health, University of California at Berkeley and the GVN; Dr. Lawrence Blatt of Aligos Therapeutics and the GVN; Dr. Angela Chang of the Danish Institute for Advanced Study, University of Southern Denmark; and, Dr. Shabaana Khader of the Department of Molecular Microbiology, Washington University in St. Louis School of Medicine.
“LAVs against tuberculosis and smallpox have been associated with better long-term survival,” said Dr. Christine Benn of the Department of Clinical Research, GVN Center of Excellence, University of Southern Denmark. “For example, OPV campaigns in West Africa have been associated with a 25% reduction in all-cause mortality, with each additional dose reducing mortality by a further 14%.”
“Several basic science observations make clear the central importance of innate immunity in controlling coronaviruses including SARS-1, SARS-CoV-2, and MERS,” said Dr. Mihai Netea of the Department of Internal Medicine and Radboud Center for Infectious Diseases, Radboud University Medical Center, a GVN Center of Excellence. “Further, control of coronaviruses by bats is largely associated with an appropriate balancing of innate immune responses between resistance and tolerance.”
“It is critically important from both scientific and public health perspectives that we complete rigorous trials evaluating the effectiveness of LAVs in preventing COVID-19 or mitigating its severity,” said Dr. Annie Sparrow of the Department of Population Health Science and Policy, Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai. “The findings from these trials will inform if, and how, we could incorporate LAVs into our toolkit against future pandemics.”
Contact
Nora Samaranayake
Director of Marketing and Public Relations
443-823-0613
nsamaranayake@ihv.umaryland.edu
Related stories

Thursday, April 27, 2023
Current HIV Research: Milestones: Dr. Robert C. Gallo and the Discovery of HIV-1
In this issue of the journal, we inaugurate a new series entitled “Milestones.” This series will encompass interviews with some of the pioneers that have laid the foundations of HIV research. Revisiting these landmarks while taking into account the prospect of their founders should be an inspiration to our readers, particularly the youngest generation. Nobody better than Dr. Robert Gallo could be the protagonist of the inaugural “Milestone,” with his recount of the discovery of HIV-1, the causative agent of AIDS, and the development of the first blood test to diagnose HIV-1 infection.

Thursday, March 30, 2023
Living Legend Dr. Robert Gallo and His Legacy at the University of Maryland School of Medicine’s Institute of Human Virology
Dr. Robert Gallo, MD, is internationally renowned as a co-discoverer of HIV, the cause of AIDS, and as a two-time recipient of the prestigious Albert Lasker Award – a program established in 1945 to honor individuals who have made major contributions to medical science or who have performed public service on behalf of medicine.

Wednesday, March 29, 2023
Dan Rodricks: What I didn’t know about Dr. Gallo
Until this week, when I looked deeper into his background for my current Sun column, I did not know Dr. Robert Gallo’s origin story as a scientist. It was the death of his six-year-old sister, Judith, when Gallo was a boy in Connecticut, that launched his career in cancer and virus research. He went on to become one of the leading biomedical researchers in the world, the co-discoverer of HIV and a founder of both the Institute of Human Virology in Baltimore and the Global Virus Network.

Tuesday, March 28, 2023
The Baltimore Sun: Dan Rodricks: Renowned scientist Robert Gallo takes on emeritus role at Baltimore’s Institute of Human Virology
Dr. Robert Gallo, co-discoverer of the human immunodeficiency virus that causes AIDS and one of the world’s most celebrated cancer researchers, has stepped down as director of the Institute of Human Virology that he established in downtown Baltimore 27 years ago. But it’s not like the 86-year-old virologist is retiring.
Monday, March 06, 2023
Eradicating Polio Will Require Changing the Current Public Health Strategy
The recent public health emergency declarations in New York and London due to polio infections and detection of the virus in these cities’ wastewater strongly indicate that polio is no longer close to being eradicated. Now, four members of the Global Virus Network (GVN) proposed changes in global polio eradication strategy to get the world back on track to one day eliminating polio’s threat.

Tuesday, January 31, 2023
University of Maryland School of Medicine’s Institute of Human Virology Director Dr. Robert Gallo Co-Authors STAT Op-Ed with a U.S. Government Call to Action and Road Map for the Future of
STAT today published "How the Biden administration’s Covid preparedness policies could narrow America’s political divide" co-authored by leadership of the Global Virus Network (GVN), representing 68 Centers of Excellence and 11 Affiliates in 37 countries, and comprising foremost experts in every class of virus causing disease in humans and some animals. The opinion piece calls on the Biden Administration to “follow the science” in updating COVID-19 preparedness policies to align with the indefinite endemic phase the country is now facing.

Wednesday, January 18, 2023
BBC: The scientist who smuggled HIV in her bag into her country to study it and save lives
Acquired immune deficiency syndrome, AIDS, had been recognized as a new disease in 1981, when an increasing number of young homosexuals died of unusual infections and rare cancers. It was also known to affect intravenous drug users and some were known to have contracted it through blood transfusions.
Wednesday, January 18, 2023
Baltimore Banner: Hunt for infectious disease treatments takes on new urgency
When monkeypox cases began spiking in early June, some of those infected and at risk were dismayed that there weren’t proven therapies ready. There was a promising treatment, tested in animals but not humans, for the infections regularly seen in Africa but rarely reported in Europe or North America. The drug was used sparingly before the emergency began abating. But instead of putting the tecovirimat, or TPOXX, back on the shelf, researchers at Johns Hopkins and elsewhere launched a major study to confirm it worked for monekypox, now known as mpox.

Friday, January 06, 2023
USA Today: Fact check: Research proves HIV is the cause of AIDS, contrary to viral claim
The claim: There is no proof HIV is the cause of AIDS. A Dec. 15 Facebook video shows Kary Mullis, a scientist known for denying the link between HIV and AIDS, claiming again there is no proof HIV is the cause of AIDS. The post was shared more than 1,000 times in a week. The clip comes from a 2009 documentary that promoted AIDS denialism, which has more than 300,000 views on YouTube.

Tuesday, August 09, 2022
CNBC: ‘We don’t even agree on how to define it yet’: It’s year three of the pandemic and scientists still know very little about long COVID
We’ve entered year three of the pandemic, and experts still know very little about long Covid, including how to cure its symptoms. On July 20th and July 21st, the Global Virus Network hosted the first-ever conference devoted solely to the science of long COVID. There, scientists spoke openly about what is known about the mysterious condition and the questions that remain.

Monday, July 25, 2022
Institute of Human Virology at the University of Maryland School of Medicine Supports First-of-Its-Kind Conference to Evaluate the Public Health Magnitude of Long COVID And Define A Global R
The conference, hosted at the University of Maryland, Baltimore, reviewed the wealth of cohort data on long COVID, constructed a framework to characterize and define the conditions, and identified the most critical and urgent areas of research needed to better understand, diagnose, and treat this developing public health crisis.

Friday, July 22, 2022
STAT: ‘There’s no one long COVID’: Experts struggle to make sense of the continuing mystery
Presented by the Global Virus Network, a coalition of leading virologists, the two-day virtual conference convened at the University of Maryland, Baltimore where experts across disciplines and around the world to ask and answer questions about what causes long COVID, how to predict who gets it, how to treat it, and just possibly how to prevent it.

Tuesday, May 24, 2022
Baltimore Sun: Monkeypox ‘isn’t COVID,’ but CDC still wants public to be aware of cases
Officials from the U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention warned the public and medical providers Monday to be on alert for possible cases of monkeypox as it counts up to five cases of the normally rare disease around the nation. But the officials say the threat to the general public remains low, as it’s just not as easily spread as other diseases such as COVID-19. Rather, it takes touching or sharing fluids with someone with the characteristic monkeypox rash.

Thursday, May 19, 2022
Baltimore Sun: With COVID cases rising, you’re still not fully vaxxed or boosted? Come on now.
Dan Rodricks: I recently had conversations with a middle-aged man who is extremely careful about what he puts into his body. He eats lots of fruits and vegetables and stays away from red meat and processed foods. He also refuses to get the vaccine against COVID-19, even as infections are on the rise again.

Tuesday, April 12, 2022
'Live' Polio Vaccine Fires Up Immune System Providing Protection from SARS-CoV-2 Infection
Two new studies from the Global Virus Network, including the University of Maryland’s Institute of Human Virology and in partnership with the Petroleum Industry Health Organization of Iran, provide evidence that getting the oral polio vaccine made from live, weakened polio-virus may protect people from COVID-19 infection by stimulating the immune system.

Tuesday, April 05, 2022
UM School Of Medicine Institute of Human Virology’s Robert Gallo Receives Distinguished Alumni Award by the University of Chicago Medical Association
Robert Gallo, MD, The Homer & Martha Gudelsky Distinguished Professor in Medicine, Co-Founder and Director of the Institute Human Virology at the University of Maryland School of Medicine and Co-Founder and Chair of the Scientific Leadership Board of the Global Virus Network, was awarded the Distinguished Alumni Award by the University of Chicago Medical & Biological Sciences Alumni Association (UChicago MBSAA) for his lifetime achievements. Honorees will participate in a panel discussion on May 10 and will be presented the award on May 21 at the Hyde Parke campus.

Friday, March 18, 2022
Deutsche Presse-Agentur: Virus hunt for decades: US researcher Robert Gallo turns 85
Few scientists in the world can come up with as many successes as Robert Gallo: The US researcher was involved in the discovery of the AIDS virus, found leukemia pathogens and other deadly viruses. Now he is 85 - and works even harder than before.

Thursday, March 10, 2022
Healthline: HIV-1 May Be More Virulent When Transmitted Through Penile-Vaginal Intercourse
HIV-1 can be transmitted through vaginal, anal, and oral sex, whether it’s with a same-sex or different-sex partner. But the risk of developing it seems to vary depending on how the disease is transmitted. In fact, the HIV virus may be more virulent when passed between male and female partners who have penile-vaginal sex than among men who have anal sex with other men, according to a new study from the Indian Institute of Science.

Wednesday, February 23, 2022
TIME: Knowing the Origins of COVID-19 Won't Change Much
Over two years since the first cases started appearing in Wuhan, China, there is much we don’t know about the origins of SARS-CoV-2, the virus causing COVID-19. But a quick resolution to that question is possible: scientists could find bats in a cave somewhere in China or in southeast Asia and trace a chain leading from those bats to the COVID-19 outbreak in Wuhan. Realistically, however, recent history offers little promise for this to happen quickly.

Wednesday, February 16, 2022
WBAL: Maryland HIV researcher on latest research: It's not a cure
Scientists used a cutting-edge stem cell transplant method to treat a woman's HIV, but a lead researcher in Maryland said it's too soon to celebrate. A U.S. woman is the third known person who is in HIV remission after receiving stem cells from umbilical cord blood, an American research team announced Wednesday.

Tuesday, February 08, 2022
The New Yorker: Beyond the Booster Shot
Could a “broad spectrum” booster increase our immunity to many pathogens simultaneously? The first tuberculosis vaccine was developed in 1921, by two French scientists, Albert Calmette and Camille Guérin. It was called Bacillus Calmette-Guérin, or B.C.G., and has long been one of the world’s most widely administered shots. From the beginning, its power was surprising. B.C.G. contains a bacterium similar to the one that causes TB, and engenders an immune defense specific to that disease. But, as Calmette noted in a paper in 1931, those vaccinated with B.C.G. at birth were around seventy-five per cent less likely to die in their early years of any cause.
Wednesday, January 26, 2022
STAT: Early research suggests cancer drug could help flush HIV from its hiding spots
In a study published Wednesday in Science Translational Medicine, researchers looked at 32 patients that had both cancer and HIV and found that pembrolizumab, which revives the immune system and encourages it to attack tumors, also has the ability to flush HIV out of its hiding spot in immune cells.

Tuesday, January 25, 2022
Baltimore Sun: Doctors in Maryland see COVID treatments aiding return to more normal life, once the public can get them
The focus is increasingly on preventing hospitalizations and deaths, rather than stopping all COVID-19 infections, by using new therapies.

Monday, January 10, 2022
Yahoo! Finance: Adamis Pharmaceuticals Submits Fast Track Application to FDA for Tempol for the Treatment and Prevention of COVID-19
Although recent oral antiviral drugs have been approved by the FDA, the Company believes that Tempol would provide an unmet medical need because of its unique mechanism of action and safety profile.

Tuesday, January 04, 2022
Economy.bg: What do scientists want for 2022?
Economy.bg asked scientists from Bulgaria and the world what they hope for in 2022.

Wednesday, December 22, 2021
Economy.bg: The year through the eyes of scientists
Economy.bg asked scientists in our country and around the world what they think is the most important of the past 2021

Thursday, December 16, 2021
Ren TV (Russia): Virologist who discovered HIV urged to vaccinate children
Robert Gallo, director and co-founder of the Institute of Human Virology at the University of Maryland and co-founder of the Global Virus Network, discussed why it is important to vaccinate children against coronavirus.

Tuesday, November 02, 2021
CNN: Johnson & Johnson's Covid-19 vaccine is 73.6% effective, according to new real-world study
In an accompanying commentary, Dr. Mohammad Sajadi of the Institute of Human Virology at the University of Maryland School of Medicine, argued that the findings are part of a growing body of work that suggests "room for improvement" with the J&J vaccine.

Tuesday, October 26, 2021
Correio Braziliense: "It's obvious that no vaccine causes AIDS," says one of the virologists who discovered HIV
The virologist, and one of the discoverers of HIV, speaks to Correio about statements by President Bolsonaro live on social media

Friday, October 22, 2021
Healthline: Why Unvaccinated People Are Being Denied Organ Transplants
Experts say there are a number of reasons they prefer organ transplant recipients receive vaccinations against COVID-19 as well as other diseases before surgery.
Thursday, September 02, 2021
Yahoo! Finance: Adamis Pharmaceuticals Doses First Patients in Phase 2/3 Clinical Trial for Tempol in the Treatment of COVID-19
Adamis Pharmaceuticals Corporation announced the initiation of patient dosing in the Phase 2/3 clinical trial for Tempol, an oral antiviral product candidate, in adult patients with confirmed COVID-19 infection. In preclinical studies, Tempol has been shown to have antiviral, anti-inflammatory and antioxidant activity.

Monday, August 16, 2021
Maryland Public Television: On Who Needs COVID Booster Shots
Dr. Katya Prakash-Haft discusses why organ transplant recipients and other immune compromised people need COVID booster shots
Friday, August 13, 2021
WMAR: CDC Recommends Third Shot for Immunocompromised Americans
The federal agency’s decision follows the FDA’s move to authorize the additional shot of the Pfizer and Moderna vaccine. It comes after research has shown the vaccine isn’t as effective for immunocompromised people compared to the general population.

Monday, July 26, 2021
WJLA: Amid virus surge, Fauci says some might 'likely' need booster shots
As COVID-19 cases surge and the highly infectious delta variant spreads across the United States, drugmakers and federal health officials remain divided over when and if people who have been vaccinated might need booster shots to bolster their immunity.

Friday, July 23, 2021
Newswise: COVID Variants and a Surge Among the Unvaccinated
Panelists will discuss the threat posed by new COVID variants and continued vaccine hesitancy.

Friday, July 23, 2021
WUSA: VERIFY: Here's a look at Japan's vaccination plan
People online claim the Olympics are in jeopardy because the country has no plan to vaccinate its population. That's false.

Thursday, July 08, 2021
Bloomberg News: Dr. Gallo Says COVID-19 Is a Solvable Problem
Dr. Robert Gallo, The Global Virus Network Co-founder and Director at University of Maryland says COVID-19 is a solvable problem, as obviously it was easy to get a solvable vaccine.

Saturday, July 03, 2021
India Today: Exclusive: Virologist Dr. Robert Gallo Speaks On Third Wave, Effects On Children & Other COVID Issues
Will India and the world see a third wave, if yes then when? How much the third wave will affect children? If mRNA vaccine is the future of COVID-19 vaccines? World's top virologist, Dr. Robert Gallo, answers these and many other questions related to COVID-19 and its vaccination in an exclusive conversation with Rajdeep Sardesai.

Friday, June 25, 2021
Doctor Radio: What We Know About the Virology of COVID-19
Dr. Marc Siegel talks to the Co-founder & Director of the Institute of Human Virology at the University of Maryland School of Medicine and Co-founder for the Global Virus Network, Dr. Robert Gallo, as well as the President of the Global Virus Network, Dr. Christian Brechot, about COVID-19 Origin, Immunity, Vaccines, and Variants.
Friday, June 25, 2021
Weather Channel: Mystery Thickens Over COVID-19's Origin; Claims of Hidden Early Genetic Information Attracts Further Scrutiny
COVID-19 pandemic has been wreaking worldwide havoc for nearly 20 months now. Yet, Its origin and early spread continue to be one of the most intriguing scientific puzzles of recent history. Claims that the earliest coronavirus strains leaked out from a lab in the Wuhan Institute of Virology in China have resurfaced and subsided multiple times, throughout the course of the pandemic. While many such claims were eventually disregarded as unfounded speculations of conspiracy theorists, allegations have continued against the Wuhan lab having known about the infection and its subsequent threat, much before the world at large was aware.

Tuesday, June 22, 2021
The Washington Post: Wuhan lab’s classified work complicates search for pandemic’s origins
The Wuhan lab has drawn global scrutiny because of its research on bat coronaviruses in the city where the pandemic began. The events have shined a light on a research niche that — in China, the United States and elsewhere — operates with heightened secrecy because of the national security risks of handling deadly pathogens.

Monday, June 21, 2021
Reuters: India should brace for third COVID-19 wave by Oct, say health experts
A third wave of coronavirus infections is likely to hit India by October, and although it will be better controlled than the latest outbreak the pandemic will remain a public health threat for at least another year, according to a Reuters poll of medical experts.

Thursday, June 17, 2021
Big Biology Podcast: Old vaccines for new pandemics (Episode 66)
What has COVID-19 taught us about preparing for future epidemics? Can we trigger innate immune responses – our first lines of defense - to mitigate novel infections? Can we use live-attenuated vaccines (LAV) meant for other infections to protect us while we develop specific vaccines for new pathogens? On this episode, we talk to virologists Konstantin Chumakov and Robert Gallo about their recent paper entitled “Old vaccines for new infections”.

Thursday, June 03, 2021
Slate: A Very Calm Guide to the Lab Leak Theory
More than a year into the COVID-19 pandemic, scientists still aren’t sure where exactly the virus that caused this mess came from, and how it was able to spread so rapidly among humans. With the origins of the coronavirus still up in the air, there’s been a lot of talk of the so-called lab leak theory—the idea that the virus spread to people in a laboratory accident, rather than jumping from a wild animal to a human. In recent days, there’s been a flurry of speculation, and it can be hard to parse what the lab leak theory is all about, how likely it is, and why it matters at all. Here’s our attempt to sort some of that out.

Tuesday, June 01, 2021
SciDevNet: ‘Old vaccines can fight new pandemics like COVID-19’
Inoculation with live attenuated vaccines (LAV) such as those used against TB, polio or measles can stimulate the immune system to provide protection against other infectious diseases, including COVID-19, says a new study. People who have been inoculated with one or more LAVs but have no access to the new, specific vaccines against COVID-19 — typically because they are expensive or in short supply — may have some protection during the current pandemic, according to the study.
Thursday, May 27, 2021
Baltimore Sun: Maryland researchers study whether HIV cure can come from infusing patients with genetically modified ‘super T cells’
A week ago, a Washington, D.C., man in his 30s with HIV became the first person to be infused with a heaping load of his own genetically modified cells that a Maryland biotech firm believes one day could lead to the elusive cure for the disease. American Gene Technologies’ method involves taking T cells out of a person’s blood and genetically modifying them in the lab to resist infection before they are reinfused. C. David Pauza is the company’s chief science officer and a former professor and researcher at the University of Maryland School of Medicine’s Institute for Human Virology. Another center evaluating entering the study is Maryland’s Institute for Human Virology, confirmed its co-founder and director, Dr. Robert Gallo, who is internationally regarded for his role in discovering HIV and developing a blood test to detect it.

Monday, April 19, 2021
Bloomberg TV: Will Vaccines Protect Us From All Covid-19 Variants?
Dr. Robert Gallo, co-founder of the Global Virus Network and director of the Institute of Human Virology at the University of Maryland School of Medicine, discusses the global rollout of Covid-19 vaccines. Global cases passed 141 million, and deaths exceeded 3 million. Gallo speaks with Haidi Stroud-Watts and Shery Ahn on "Bloomberg Daybreak: Australia."

Monday, April 19, 2021
China Business Network: An interview with Dr. Gallo on COVID-19, Variants and Vaccines
In an exclusive interview with CBN, Dr. Robert Gallo, a world-renowned virus expert, speculated that certain components of Johnson & Johnson and AstraZeneca vaccines may induce the immune system to produce an antibody, which can cause a very small number of people. Heparin-induced thrombocytopenia, thrombosis.

Friday, April 09, 2021
Aljazeera: Which vaccine is best? The one you can get first, experts say
As the United States ramps up its COVID-19 inoculation campaign, aiming to make vaccines available to all adults by April 19, some doctors and health workers are concerned that brand preferences among potential vaccine recipients could hurt attempts to slow the spread of the virus.

Thursday, April 08, 2021
Fox 5 DC: Experts weigh in on timing for second covid-19 vaccine doses
Just how important is timing when it comes to the second dose of the Pfizer and Moderna vaccines? Walgreens is now adjusting its vaccine scheduling process after being asked to do so by the CDC. They were spacing Pfizer vaccines 28 days apart instead of recommended 21 days, because it was just easier to schedule them the same as the Moderna shot.

Thursday, April 01, 2021
Associated Press: Can I still spread the coronavirus after I’m vaccinated?
Can I still spread the coronavirus after I’m vaccinated? It’s possible. Experts say the risk is low, but are still studying how well the shots blunt the spread of the virus. The current vaccines are highly effective at preventing people from getting seriously sick with COVID-19.

Tuesday, February 16, 2021
The Baltimore Sun: Maryland sees little flu this season as researchers wonder if flu vaccine staves off COVID-19
February is typically the cruelest month for the flu with thousands of infections, hundreds hospitalized and some dying in Maryland. Not this year. Due in part to the coronavirus pandemic and preventative measures associated with it, the influenza virus is downright rare in Maryland and across the nation. But researchers are wondering if there’s a chance that the flu shot you got in the fall may yet fend off a nasty infection — of COVID-19.

Friday, February 12, 2021
The Washington Post: Scientists said claims about China creating the coronavirus were misleading. They went viral anyway.
The spread of the unverified assertions by Chinese scholar Li-Meng Yan, widely dismissed as “flawed,” show how vulnerable scientific sites are to misuse and misunderstanding.

Thursday, February 04, 2021
WTOP NEWS: What a new U.Md. study says about skipping second doses of COVID-19 vaccine
None of the trials conducted on the Moderna and Pfizer-BioNTech vaccines tested them on people who already had been infected by the coronavirus. Now, a study involving people previously infected with COVID-19 suggests the immune response from getting sick may act like getting a first dose of those double-shot vaccines.

Tuesday, February 02, 2021
Business Insider: People who had COVID-19 may develop 10 times more antibodies after a single vaccine dose - a sign they might only need one shot
Business Insider - People who had COVID-19 developed at least 10 times more antibodies after their first vaccine dose than the average uninfected person who received two doses, new research shows. Another preliminary study similarly found that healthcare workers who had COVID-19 responded to their first shot the way most people respond to their second. The researchers both suggested that post-COVID patients may only need one shot to sufficiently protect them from the disease again.
Tuesday, February 02, 2021
The Baltimore Sun - People who’ve had COVID-19 may not need both doses of the vaccine, University of Maryland study suggests
The Baltimore Sun - A study by researchers at the University of Maryland School of Medicine suggests that people who have already had COVID-19 may not need both doses of the vaccine to be protected from the virus. The emerging research comes as states, including Maryland, face continued vaccine shortages, leaving the growing list of eligible patients to scramble for few available appointments. But experts say that withholding second doses could present logistical obstacles for an already challenged process.

Monday, December 21, 2020
Robert Gallo of the UM School of Medicine Institute of Human Virology and Global Virus Network Awarded Top Life Sciences and Medicine Prize from China
Robert C. Gallo, MD, The Homer & Martha Gudelsky Distinguished Professor in Medicine, co-founder and director of the Institute Human Virology at the University of Maryland School of Medicine and co-founder and international scientific advisor of the Global Virus Network, was awarded the “VCANBIO Award for Biosciences and Medicine,” a significant and authoritative award in the life sciences and medicine field of China. The elite Prize is jointly presented by the University of Chinese Academy of Sciences and the VCANBIO CELL & GENE ENGINEERING CORP, LTD to push forward scientific research, technological innovation and continuous development in the life sciences and medicine field of China.

Friday, December 18, 2020
UMSOM Institute of Human Virology's Robert Gallo Awarded Italy's Magna Graecia International Prize
Robert Gallo, MD, The Homer & Martha Gudelsky Distinguished Professor in Medicine, co-founder and director of the Institute Human Virology at the University of Maryland School of Medicine and co-founder and international scientific advisor of the Global Virus Network, was awarded Italy’s “Magna Graecia International Prize,” an award created in 1997 by the Magna Graecia Foundation that is bestowed to the most influential Italians and Italians of origin who have embodied and symbolized, in the most diverse sectors, the best qualities of Italy by extending Italian culture beyond national borders.

Friday, December 11, 2020
Bloomberg TV Asia: Dr. Robert Gallo on COVID-19 Vaccines
Dr. Robert Gallo, co-founder and international scientific advisor of the Global Virus Network and the co-founder and director of the Institute of Human Virology at the University of Maryland School of Medicine, discusses the rollout of the Covid-19 vaccines. The first Covid-19 vaccine expected to be deployed in the U.S. won the backing of a panel of government advisers, a step that will likely help clear the way for emergency authorization by the Food and Drug Administration. Gallo, who co-discovered HIV as the cause of AIDS in 1984, speaks with Haidi Stroud-Watts and Shery Ahn on "Bloomberg Daybreak: Australia." (Source: Bloomberg)

Thursday, October 08, 2020
NPR: Could The Live Flu Vaccine Help You Fight Off COVID-19?
In case you were still procrastinating getting a flu shot this year, here's another reason to make it a priority. There's a chance the vaccine could offer some protection against COVID-19 itself, says virologist Robert Gallo, who directs the Institute of Human Virology at the University of Maryland School of Medicine and is chairman of the Global Virus Network.

Wednesday, September 30, 2020
GVN’s Top Virus Experts Meet Together To Identify Most Promising Advances To Battle COVID-19 & Strategies To Prepare For Future Pandemics
Rapid Diagnostic Testing, Repurposing Drug Therapies and Vaccines Targeting Innate Immunity, Are Integral Factors in Mitigating COVID-19. The Global Virus Network (GVN), a coalition of the world’s leading medical and basic virology research centers working to prevent illness and death from viral disease, convened a press conference with attendees from across the globe to discuss key takeaways from the GVN virtual 2020 Special Annual Meeting held September 23-24, 2020.

Tuesday, September 29, 2020
NPR: Scientists Experiment With TB Vaccine To See If It Slows Spread Of COVID-19
As scientists race to develop a vaccine specific for COVID-19, some researchers are testing an old vaccine, that's been proven safe and is cheap to manufacture, to see if it could slow the pandemic.

Thursday, September 24, 2020
Baltimore Sun: A vaccine will help, not end coronavirus pandemic, experts in Maryland and globally say
A global group of virus experts warned Thursday about relying too much on the first vaccines to end the coronavirus pandemic. “If we get a perfect vaccine, great, but that’s unlikely,” said Dr. Robert Gallo, co-founder of the Global Virus Network, during a news conference following a meeting of the organization that works to understand and treat infectious diseases.
Friday, August 21, 2020
Institute of Human Virology and Italian Researchers identify a SARS-CoV-2 Viral Strain with Deletion in a Protein, Possibly Reducing Fatalities
The Institute of Human Virology (IHV) at the University of Maryland School of Medicine, a Global Virus Network (GVN) Center of Excellence, in collaboration with scientists from Campus Biomedico in Rome, Italy announced today the results of studies showing the emergence of a SARS-CoV-2 viral strain with a deletion in a protein known as nsp1. These data, accepted for publication today by the Journal of Translational Medicine, (link here) may indicate the emergence of a less pathogenic viral strain.

Monday, July 20, 2020
NPR: Early Oxford-AstraZeneca Coronavirus Vaccine Data 'Encouraging,' Scientists Say
Dr. Robert Gallo is quoted about an experimental vaccine candidate being developed by AstraZeneca and Oxford University to protect against COVID-19 that triggered an immune response against the coronavirus and appeared to be safe.

Friday, July 03, 2020
KUSI San Diego News: Dr. Robert Gallo suggests an oral polio vaccine could help fight coronavirus
Dr. Robert Gallo from the Institute of Human Virology at the University of Maryland School of Medicine and Global Virus Network wrote an op-ed in the Wall Street Journal earlier this week. The opinion piece stated that OPV, oral polio vaccine, could be a cheap and effective way to fight coronavirus. Dr. Gallo discussed his opinion piece on Good Morning San Diego.

Thursday, July 02, 2020
13D Global Strategy & Research Report
COVID-19 outbreaks are multiplying and immunity may be short-lived. Could existing “live” vaccines, which stimulate innate immunity, outshine vaccines targeting the “spike” protein?
Tuesday, June 30, 2020
Wall Street Journal Op-Ed: An Old Vaccine May Help Against Coronavirus: A tablet for polio boosts innate immunity, which fights other viruses.
In this op-ed coauthored by Dr. Robert C. Gallo and Daniel J. Arbess, they discuss how “An Old Vaccine May Help Against Coronavirus: A tablet for polio boosts innate immunity, which fights other viruses.”

Monday, June 29, 2020
Baltimore Magazine Special Edition: Dr. Gallo Featured
Dr. Robert Gallo is featured in Baltimore Magazine's special edition, "On the Front Lines: Acts of Courage and Kindness in the Age of Coronavirus."
Thursday, June 25, 2020
The New York Times: Dr. Robert Gallo: The Case for a Stopgap Vaccine
In a letter to the editor to The New York Times entitled, "Dr. Robert Gallo: The Case for a Stopgap Vaccine," the noted virologist and head of the IHV says a polio vaccine may be an ideal solution until we find a Covid-specific vaccine.
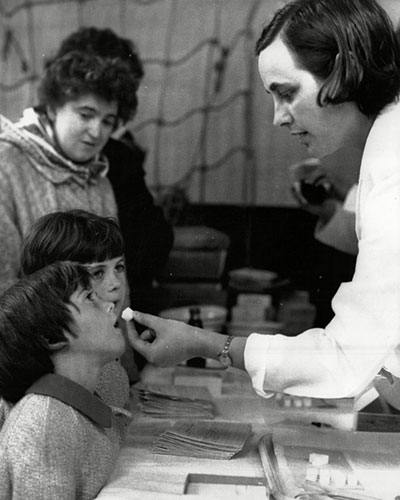

Wednesday, June 24, 2020
The New York Times: Decades-Old Soviet Studies Hint at Coronavirus Strategy
The New York Times: Decades-Old Soviet Studies Hint at Coronavirus Strategy: A married pair of virologists in Moscow tested a vaccine on their own children in the 1950s. Now, a side effect they found is sparking new hope for a defense against the coronavirus.

Tuesday, June 23, 2020
France 24: Dr. Mohammad Sajadi Speaks with France 24 on COVID-19 and Seasonality
Does Covid-19 spread faster in winter? Modelling by US researchers suggests the transmission of Covid-19 could be seasonal. Mohammad Sajadi, associate professor at University of Maryland School of Medicine's Institute of Human Virology, says the virus first spread in areas of low temperature and low humidity, common to winter time in temperate areas.

Friday, June 12, 2020
The Washington Post: We shouldn’t care who wins the vaccine ‘race’
Dr. Robert Gallo writes a Letter to the Editor to The Washington Post entitled, “We shouldn’t care who wins the vaccine ‘race’,” regarding their June 4 front-page article “Cold War echoes in race for vaccine,” about the “race” among nations, notably the United States, China, and Russia and other European nations for development of a vaccine against the novel coronavirus.

Thursday, June 11, 2020
Global Virus Network Suggests Oral Polio Vaccine May Provide Temporary Protection Against COVID-19
The Global Virus Network (GVN), a coalition comprised of the world’s preeminent human and animal virologists from 53 Centers of Excellence, including the Institute of Human Virology at the University of Maryland School of Medicine, and 10 Affiliates in 32 countries, published a viewpoint in Science today that the stimulation of innate immunity by live attenuated vaccines in general, and oral poliovirus vaccine (OPV) in particular, could provide temporary protection against coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19).

Tuesday, June 02, 2020
UM School of Medicine’s Institute of Human Virology Awarded Grants to Strengthen COVID-19 Response in Sub-Saharan Africa
The Center for International Health, Education and Biosecurity (Ciheb) at the University of Maryland School of Medicine’s Institute of Human Virology was awarded $4 million from the U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) to support coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) response activities in Botswana, Nigeria, Malawi, and Mozambique.
Saturday, May 09, 2020
Dr. Robert Gallo Discuss COVID-19 Research on Aljazeera News
Aljazeera discusses the status of therapy, testing and vaccine research on SARS-CoV-2/COVID-19 with Dr. Robert Gallo.

Thursday, May 07, 2020
The Disappointing Truth About Antibody Testing: There’s still a lot we don’t know about COVID-19
Dr. Robert Gallo discusses the status of COVID-19 antibody test with Vox's The Verge
Wednesday, May 06, 2020
The Coronavirus Appears to have Mutated. What Does that Mean for Contagiousness?
While small mutations in the virus's genetic code are evident, it's unclear what these changes mean for people, if anything at all.

Saturday, May 02, 2020
IHV's Dr. Robert Gallo on FOX's Full Court Press with Greta Van Susteren
Overtime: Dr. Robert Gallo talks coronavirus treatments and antibody testing.

Saturday, May 02, 2020
Dr. Robert Gallo on iHeart Radio to Discuss COVID-19
Ryan Gorman hosts an iHeartRadio nationwide special featuring experts on COVID-19-related issues, including the co-founder and director of the Institute Human Virology at the University of Maryland School of Medicine, the senior vice president for U.S. Programs & Advocacy at Save the Children, and the managing editor of the Military Times. Topics range from a discussion about why some people infected by the coronavirus are asymptomatic, while others face severe reactions and even death, to assistance for impoverished children, and a breakdown of the impact the virus is having on the U.S. military and veterans.

Friday, May 01, 2020
Could an Oral Polio Vaccine Stop the Coronavirus Pandemic?
A YouTube video by the American Chemical Society and produced by PBS.

Friday, May 01, 2020
NYT Op-Ed Features Gallo-Chumakov Oral Polio Vaccine for COVID-19 Idea
What if We Already Have a Coronavirus Vaccine? Researchers are testing whether decades-old vaccines for polio and tuberculosis could protect against infection.

Wednesday, April 29, 2020
Dr. Robert Gallo Appears on C-SPAN’s Washington Journal
Please check out Dr. Robert Gallo’s C-SPAN Washington Journal appearance today to discuss COVID-19 treatments, vaccines, the need for the Global Virus Network, and more.

Monday, April 27, 2020
Expert Breaks Down Coronavirus Research: Is it Worse than HIV? Is it Mutating?
IHV Co-Founder and Director, Robert Gallo, MD is interviewed on LBC, a radio station in the United Kingdom. Darren Adam had Professor Gallo on the line to discuss his research in the past and the work he's carrying out during the coronavirus crisis. "We have learned to live with HIV" Darren began, listing out how it has changed from a death sentence to a disease that humans can live a long life with. He wondered if this could be possibly the path we're taking with Covid-19.
Wednesday, April 22, 2020
Dr. Robert Gallo on India Today Discussing the Oral Polio Vaccine for COVID-19
IndiaToday on Twitter - “Can oral polio vaccine help in fighting #Covid19? @DrRobertCGallo responds. #NewsToday with @sardesairajdeep
Friday, April 17, 2020
Dr. Robert Gallo Discusses Repurposing the Oral Polio Vaccine on CNN
Dr. Robert Gallo discusses repurposing the oral polio vaccine, drug therapies and more on COVID-19 on CNN’s The Lead with Jake Tapper, April 17, 2020.

Monday, April 13, 2020
Can an Oral Polio Vaccine Stop COVID-19?
Please see this just released Associated Press article, “Could old vaccines for other germs protect against COVID-19?” with Dr. Robert Gallo (Institute of Human Virology at the University of Maryland School of Medicine) and Dr. Konstantin Chumakov (U.S. Food and Drug Administration), both of the Global Virus Network (GVN).

Wednesday, April 08, 2020
Institute of Human Virology Co-founder on Coronavirus Recovery, Antibody Testing, Drug Testing, Bloomberg TV
Dr. Robert Gallo, the Institute of Human Virology at the University of Maryland School of Medicine, Co-founder and director discusses the coronavirus. He speaks with Haidi Stroud-Watts and Shery Ahn on "Bloomberg Daybreak: Asia." (Source: Bloomberg)

Tuesday, April 07, 2020
A Deep Look Into The Coronavirus with Dr. Robert Gallo on WYPR (Baltimore’s local NPR station)
(WNPR) Dr. Robert Gallo has been getting to know viruses-- their targets and their weaknesses--for decades, even before he co-discovered the virus that causes AIDS in the 1980s. At the University of Maryland’s Institute for Human Virology, which he heads, Gallo is looking at the coronavirus; he joins us to share his thoughts. Gallo is also co-founder and international scientific advisor at the Global Virus Network.

Wednesday, April 01, 2020
Dr. Robert Gallo Featured on MSNBC’s 11th Hour with Brian Williams
Robert Gallo, MD, Co-Founder and Director of the Institute of Human Virology, discusses SARS-CoV-2/COVID-19, specifically, how he thinks the fight against the Coronavirus is going thus far.

Friday, October 04, 2019
Institute of Human Virology Hosts 21st Annual International Meeting of Top Scientists on Ending the HIV/AIDS Epidemic in America and the Intersection of Opioid Use Disorder
The Institute of Human Virology (IHV) at the University of Maryland School of Medicine commenced IHV2019 held Thursday, October 3 through Friday, October 4 at the Four Seasons Hotel in Baltimore, Maryland. This year “Progress in HIV/AIDS: Challenges in 2020” opened with highlights about the recent plan for "Ending the HIV Epidemic by 2030” with expert opinions by ADM Brett Giroir, MD, Assistant Secretary for Health at the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services (HHS)

Monday, August 26, 2019
Dr. Robert Gallo Featured in Malcolm Gladwell's Podcast, "Revisionist History: The Obscure Virus Club"
"Revisionist History" by Malcolm Gladwell: “The Obscure Virus Club,” featuring three prominent virologists, including Dr. Robert Gallo (as well as Dr. Ludwig Gross and Dr. Howard Temin).